API Automation Testing in 2025: Postman Scripts vs EchoAPI AI No-Code Assertions
Why Indie Hackers Should Care About API Assertions
Say you’re building an e-commerce side project. You call your login API, and it returns something like this:
{
"status": "success",
"code": 1000,
"data": {
"user_id": "U12345",
"token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9...",
"expire_time": "2025-06-01T12:00:00Z"
},
"message": "Login successful"
}
Now, before you trust this API, you need to check:
- HTTP status = 200 → request worked.
- Business code = 1000 → login success.
- Response time < 500ms → no laggy UX.
- Response body has
user_id+token→ usable result. - Content-Type = application/json → correct format.
That’s what assertions are for — they automatically validate your APIs so you don’t have to eyeball JSON responses every time.
Postman Assertions: Script-First Approach
In Postman, you add assertions in the [Tests] tab, using JavaScript.

Common Assertion Snippets
1. Status Code = 200
pm.test("HTTP 200", () => {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
2. Business Code = 1000
pm.test("Business code 1000", () => {
const json = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(json.code).to.eql(1000);
});
3. Response Time < 500ms
pm.test("Under 500ms", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.responseTime).to.be.below(500);
});
4. Must Contain user_id + token
pm.test("Contains user_id + token", () => {
const json = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(json.data).to.include.keys("user_id", "token");
});
5. Content-Type = JSON
pm.test("Content-Type JSON", () => {
pm.response.to.have.header("Content-Type", "application/json");
});
After running, you’ll see results at the bottom of Postman.

EchoAPI Upgrade: AI + Visual Assertions
If you don’t feel like coding, EchoAPI gives you two no-code options.
AI-Generated Assertions: One Click Setup
Click “AI Generate Assertions”, and EchoAPI analyzes the response + builds checks for you (status code, fields, types, etc.).
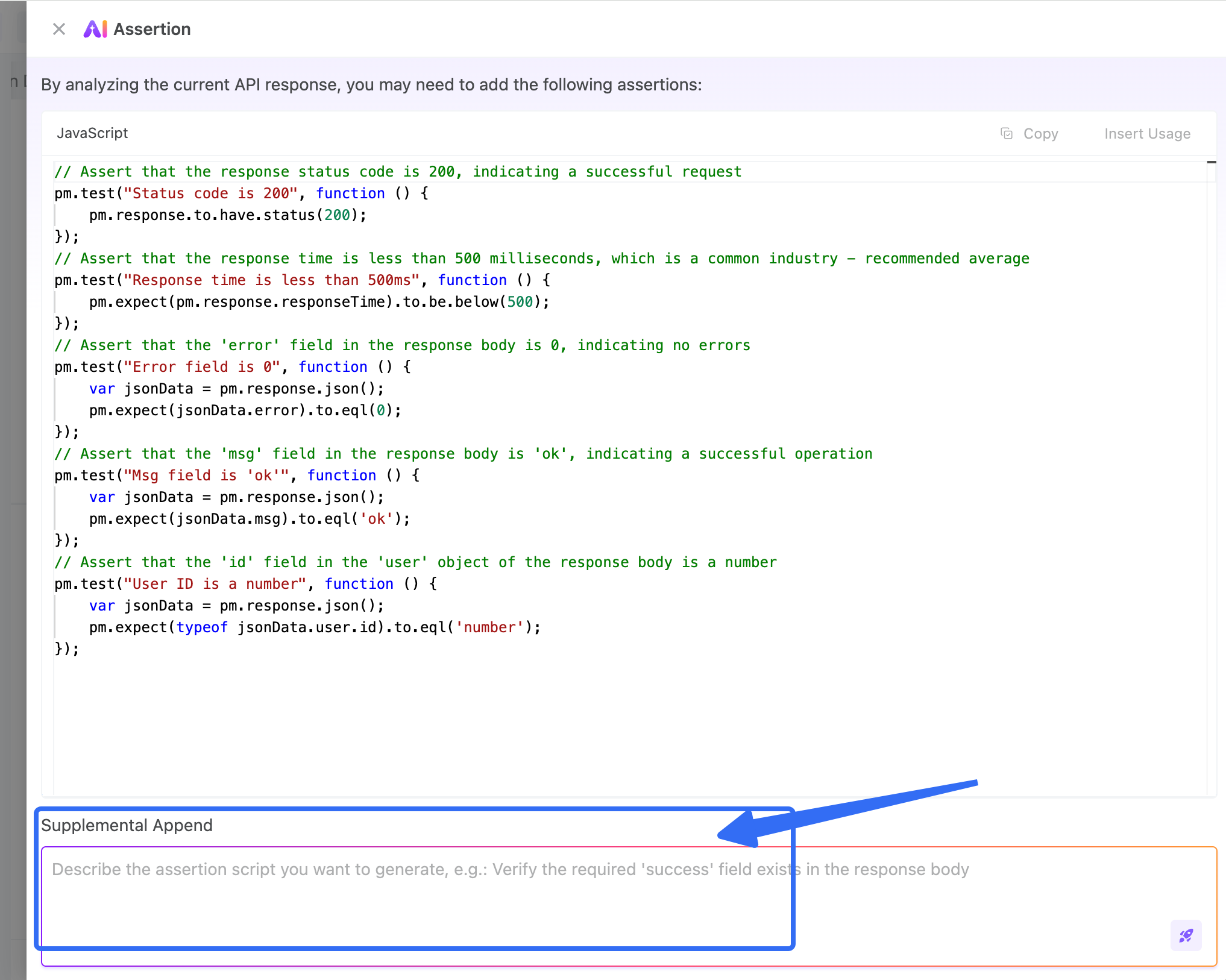
If something’s missing, just tell it:
👉 “Add a check for non-empty token”.
Visual Assertion Builder: Point & Click
With EchoAPI, you can create assertions in 3 clicks:
- Go to Post-Processing → Add Assertion.
- Pick type (Status / Response Time / Body / Header).
- Select fields visually.
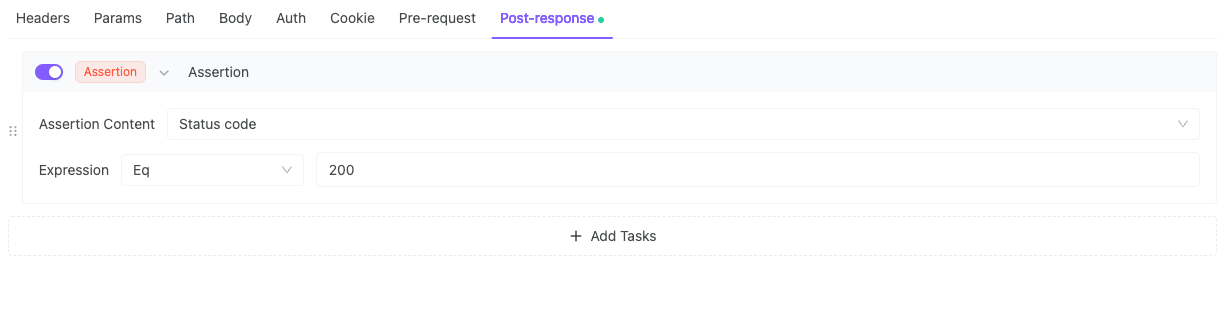
1. HTTP 200
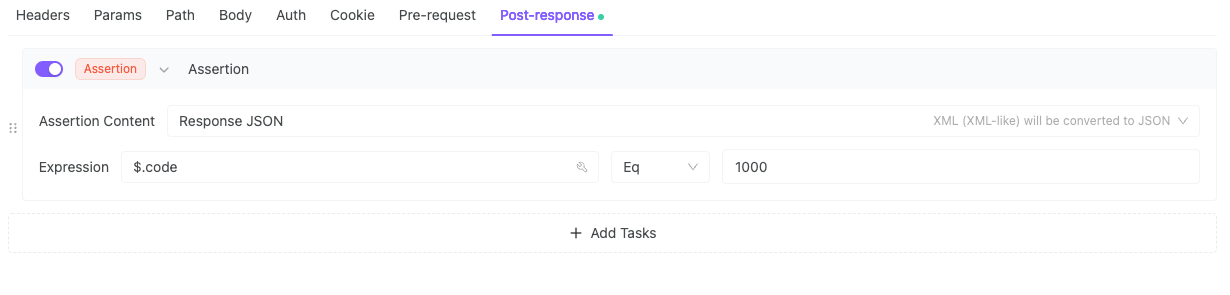
2. Business Code = 1000
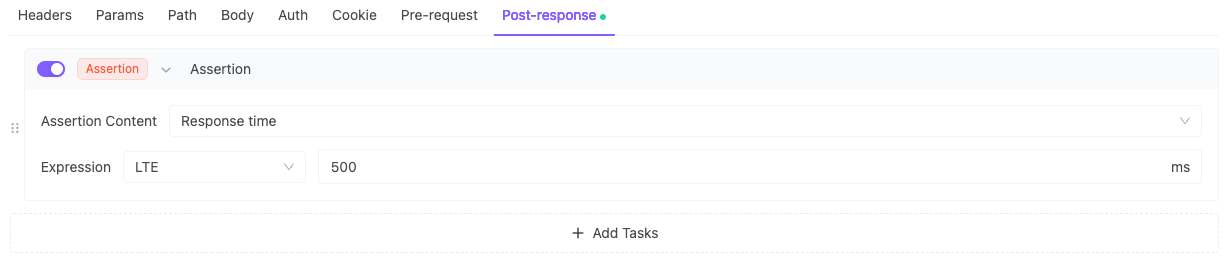
3. Response Time < 500ms
4. Must Have user_id + token
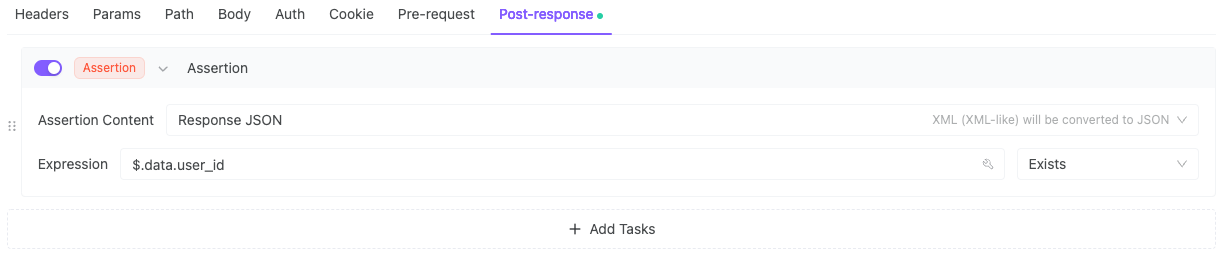
5. Content-Type = JSON
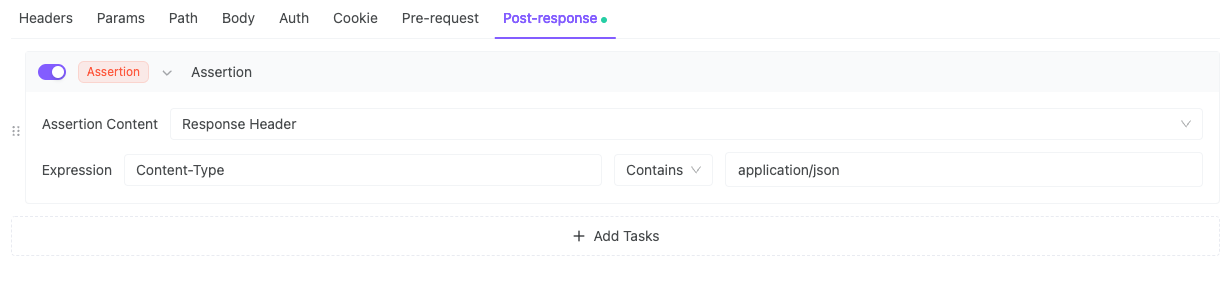
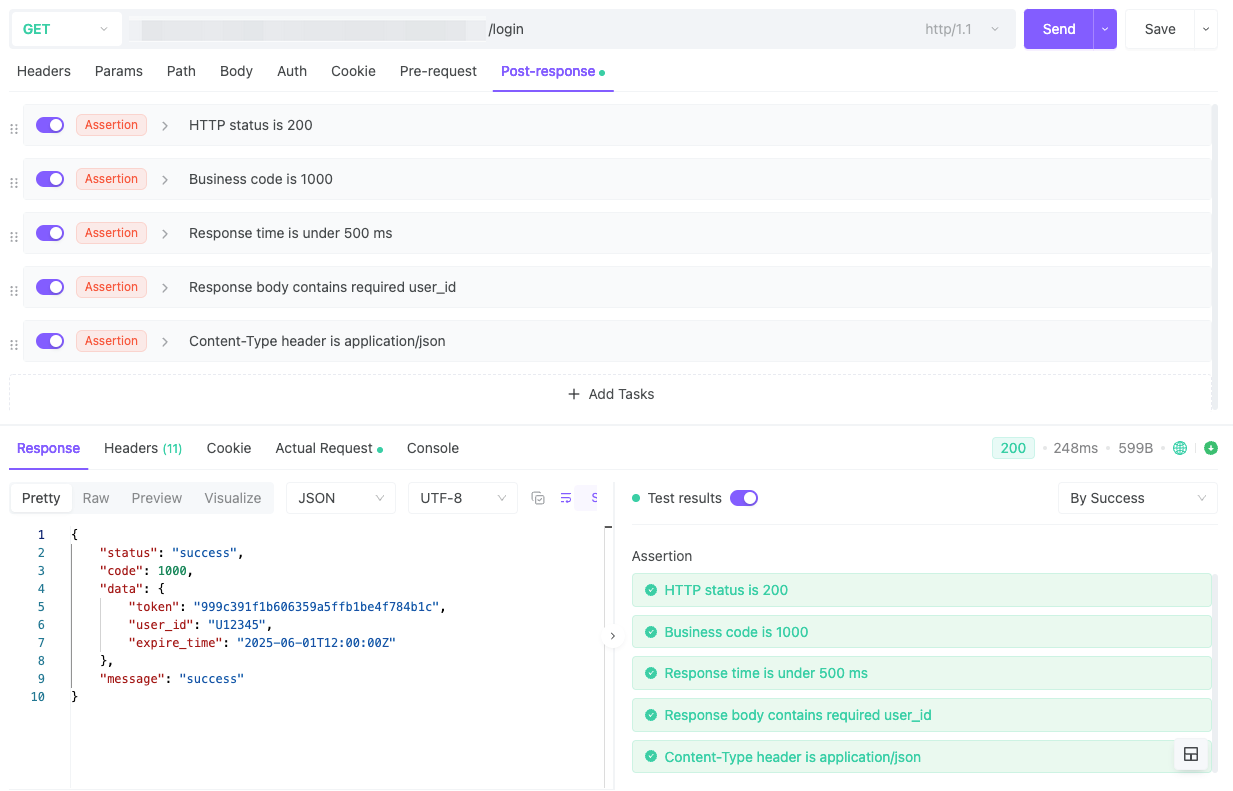
When you run tests, results show visually:
✅ Green = passed, ❌ Red = failed with error details.
Postman vs EchoAPI: Quick Comparison
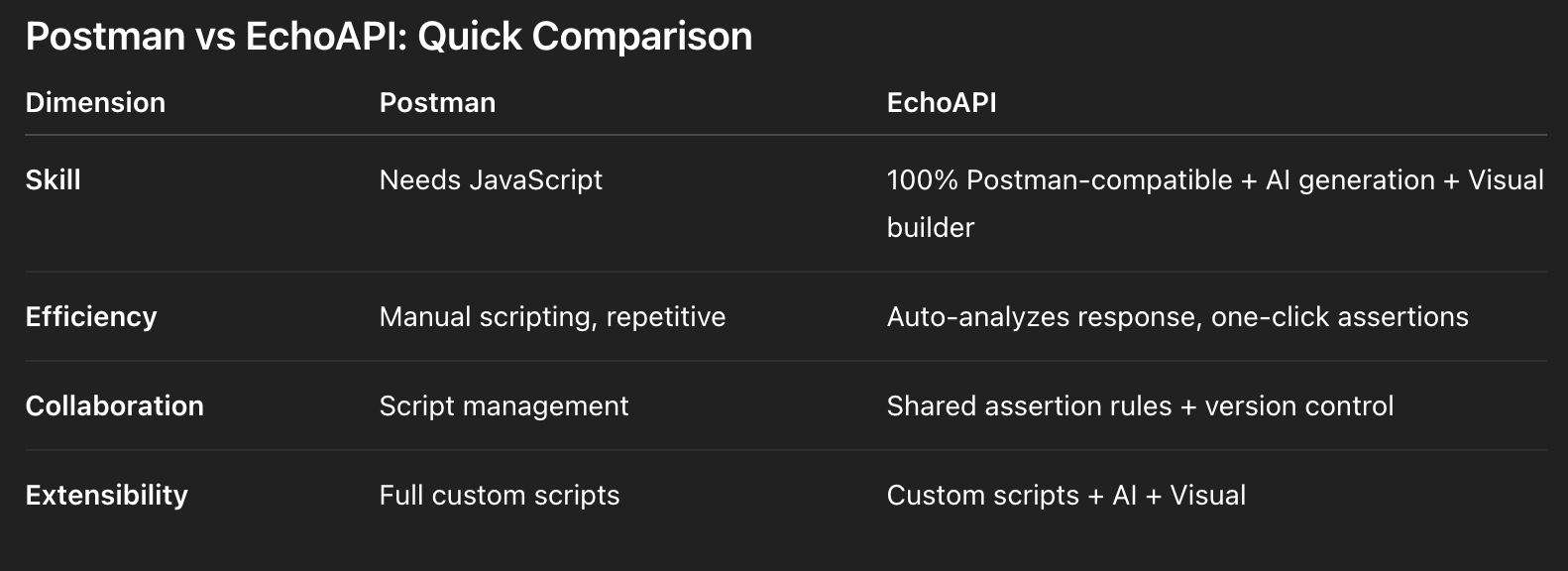
Conclusion: What Works for Indie Hackers
- If you love coding: Postman scripts = max flexibility.
- If you just want to ship fast: EchoAPI’s AI + Visual = instant setup.
- Best combo: Use EchoAPI to auto-generate baseline checks, then extend with Postman scripts if needed. They’re fully compatible.
👉 For indie hackers, this means less time debugging APIs, more time shipping features.
