Mastering OAuth 2.0: A Deep Dive into Its Core Workflows
OAuth 2.0 has emerged as the industry-standard framework for authorization, enabling secure access delegation between internet services. As digital interactions become increasingly complex and privacy concerns heighten, understanding OAuth 2.0 is essential for developers, security professionals, and businesses alike. This guide delves deeply into OAuth 2.0’s framework, explores its various flows, and highlights its significance in facilitating secure resource access across web services.

What is OAuth 2.0?
OAuth 2.0 is a protocol that allows applications to secure delegated access to user resources without sharing sensitive credentials. It enables users to grant limited access to their resources across different services with minimal friction. Major tech companies, such as Google, Facebook, Microsoft, and Twitter, have adopted OAuth 2.0, making it a cornerstone of modern web security practices. When implemented effectively, OAuth 2.0 protects user privacy and enhances security by allowing users to control what data is shared and with whom, reducing the risk of credential theft and abuse.
OAuth 2.0 Authorization Flows: A Deeper Dive
OAuth 2.0 utilizes several distinct authorization flows, each tailored to different scenarios and security contexts. Understanding these flows is crucial for implementing OAuth 2.0 correctly and securely.
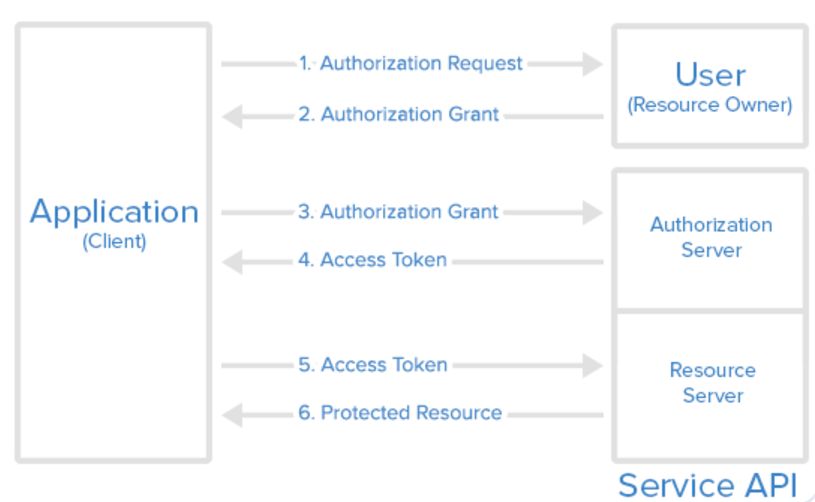
1. Authorization Code Grant
The Authorization Code Grant is the most widely used flow, especially for web applications. It offers enhanced security by requiring an additional exchange of an authorization code for an access token.
Steps:
- User Redirection: The client application redirects the user to the resource server's authorization endpoint.
- User Authentication: The user authenticates with the resource server and grants permission to the client application.
- Authorization Code: The resource server redirects back to the client with an authorization code via a specified redirect URI.
- Token Exchange: The client exchanges the authorization code for an access token by making a secure request to the resource server's token endpoint.
- Accessing Resources: The client now uses the access token to access protected resources on behalf of the user.
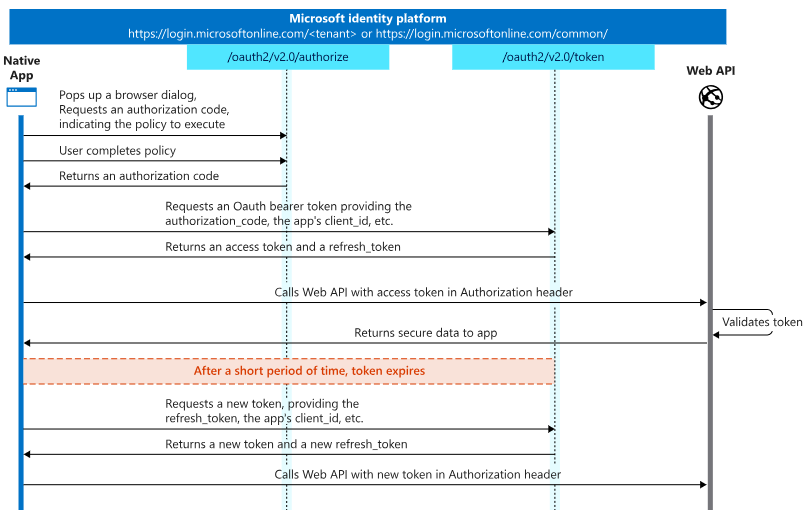
This flow is particularly suitable for applications that can keep their client secrets confidential, such as server-side web applications.
2. Implicit Grant
The Implicit Grant is designed for public clients, typically Single Page Applications (SPAs) that run in a user's browser. It issues the access token directly without the intermediate authorization code.
Steps:
- User Redirection: Similar to the Authorization Code Grant, the client redirects the user to the authorization server.
- User Authentication: The user authenticates and consents.
- Direct Token Access: Instead of an authorization code, the authorization server redirects back to the client with an access token.
- Accessing Resources: The client uses the access token directly to access resources.
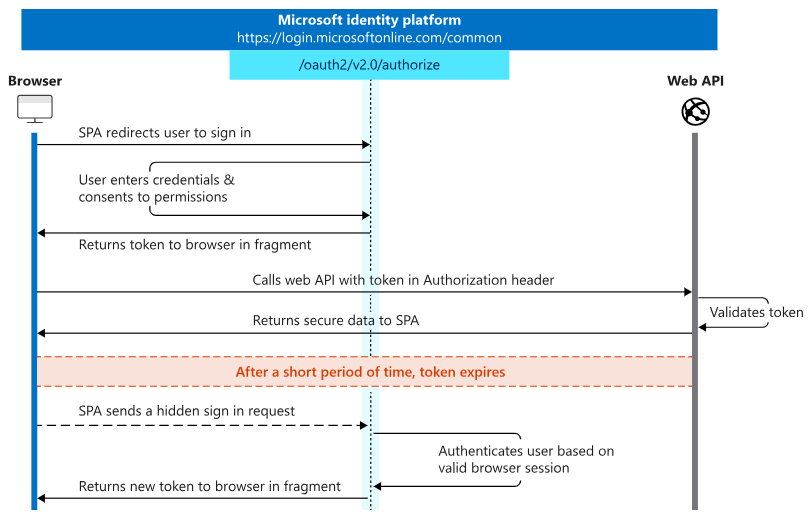
While the implicit grant is simpler for public clients, it carries a higher risk as the access token is exposed in the URL.
3. Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant
This flow is less common but useful in trusted applications where the user provides their credentials directly to the client.
Steps:
- User Credentials Input: The user enters their username and password directly into the client application.
- Token Request: The client application sends these credentials to the resource server's token endpoint.
- Retrieve Access Token: Upon successful verification, the resource server returns an access token to the client.
- Accessing Resources: The client can now access user resources with the access token.
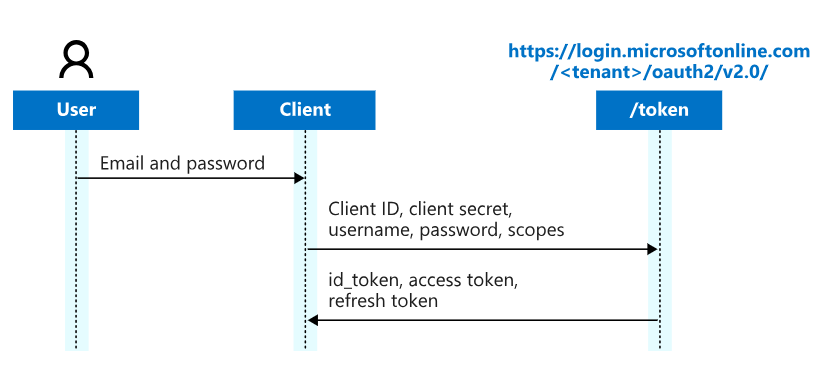
This method is only recommended when the application is highly trusted, as it requires users to share their passwords.
4. Client Credentials Grant
The Client Credentials Grant is intended for server-to-server communication where the client application acts on its behalf rather than on behalf of a user.
Steps:
- Client Authentication: The client application authenticates itself by sending its client ID and client secret to the token endpoint.
- Access Token Request: The client requests an access token without user involvement.
- Retrieve Access Token: The resource server responds with an access token.
- Accessing Resources: The client accesses resources using this token.
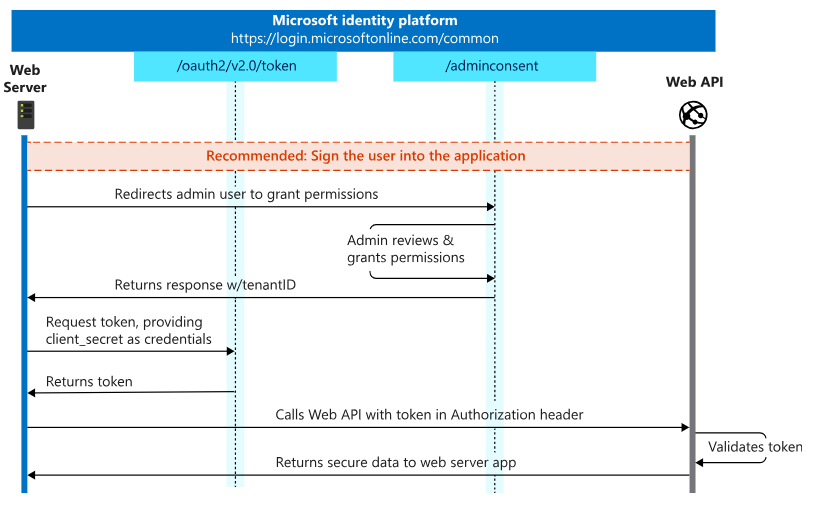
This flow is ideal for automated processes, such as backend services or microservices, where user interaction is not required.
Choosing the Right Flow
The selection among these OAuth 2.0 flows depends on factors such as the type of client, security requirements, and user experience considerations. Generally, the Authorization Code Grant is preferred for its robust balance of security and usability, especially for applications handling sensitive user data.
Simplifying OAuth 2.0 Authentication Testing with EchoAPI
Testing APIs that implement OAuth 2.0 can often be cumbersome due to the complexities involved in token retrieval and management. However, tools like EchoAPI simplify this process, allowing developers to focus on building and testing their applications efficiently.
How to Use EchoAPI for OAuth 2.0 Authentication
Step 1: Select the Authentication Type
In EchoAPI, navigate to the request setup and select the "Auth" tab. Choose "OAuth 2.0" from the authentication type dropdown menu.
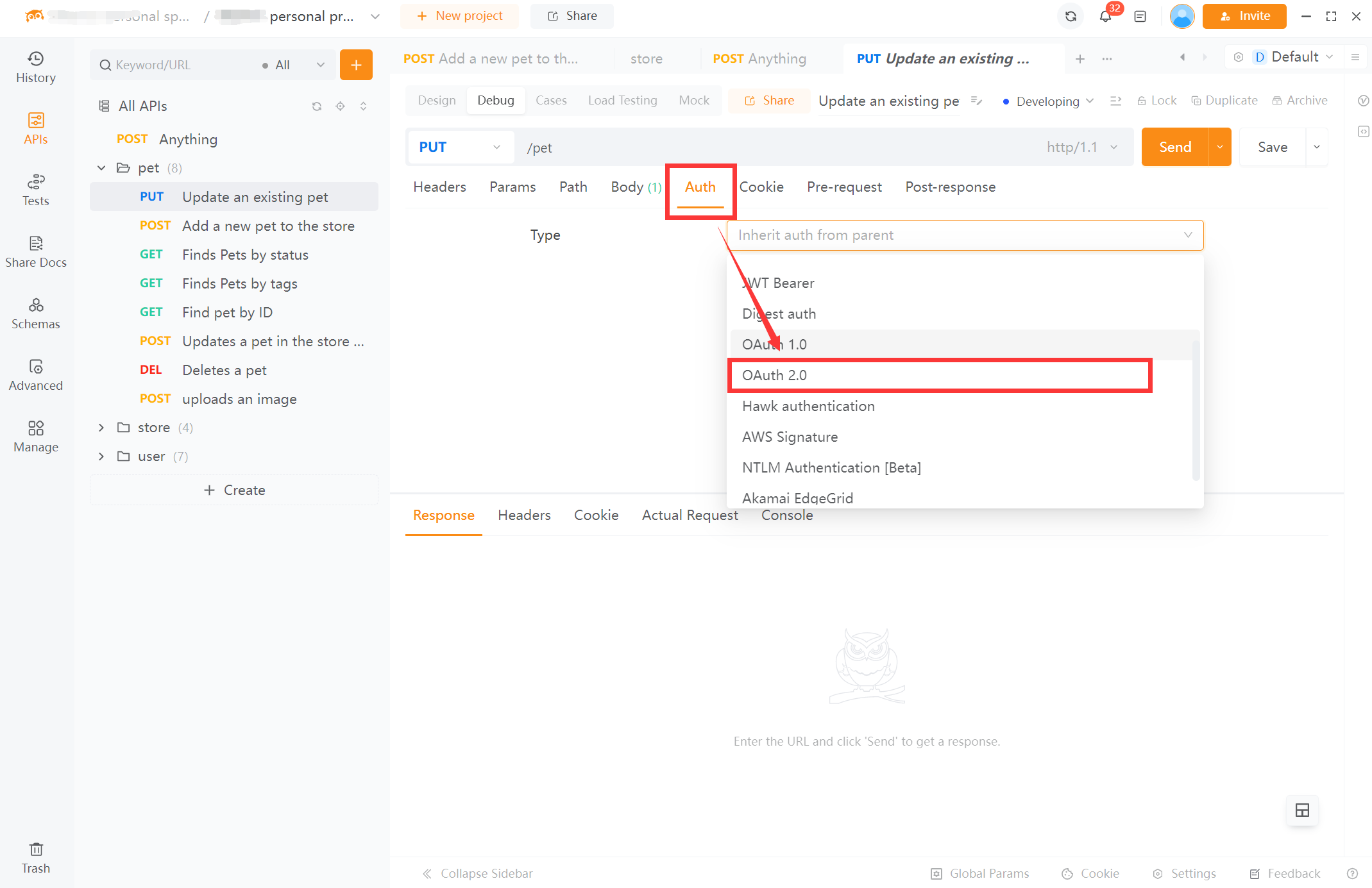
Step 2: Fill in Required Information
Enter the necessary details, such as client ID, client secret, authorization URL, token URL, and any scopes your application needs. Once completed, click the "Get Token" button.
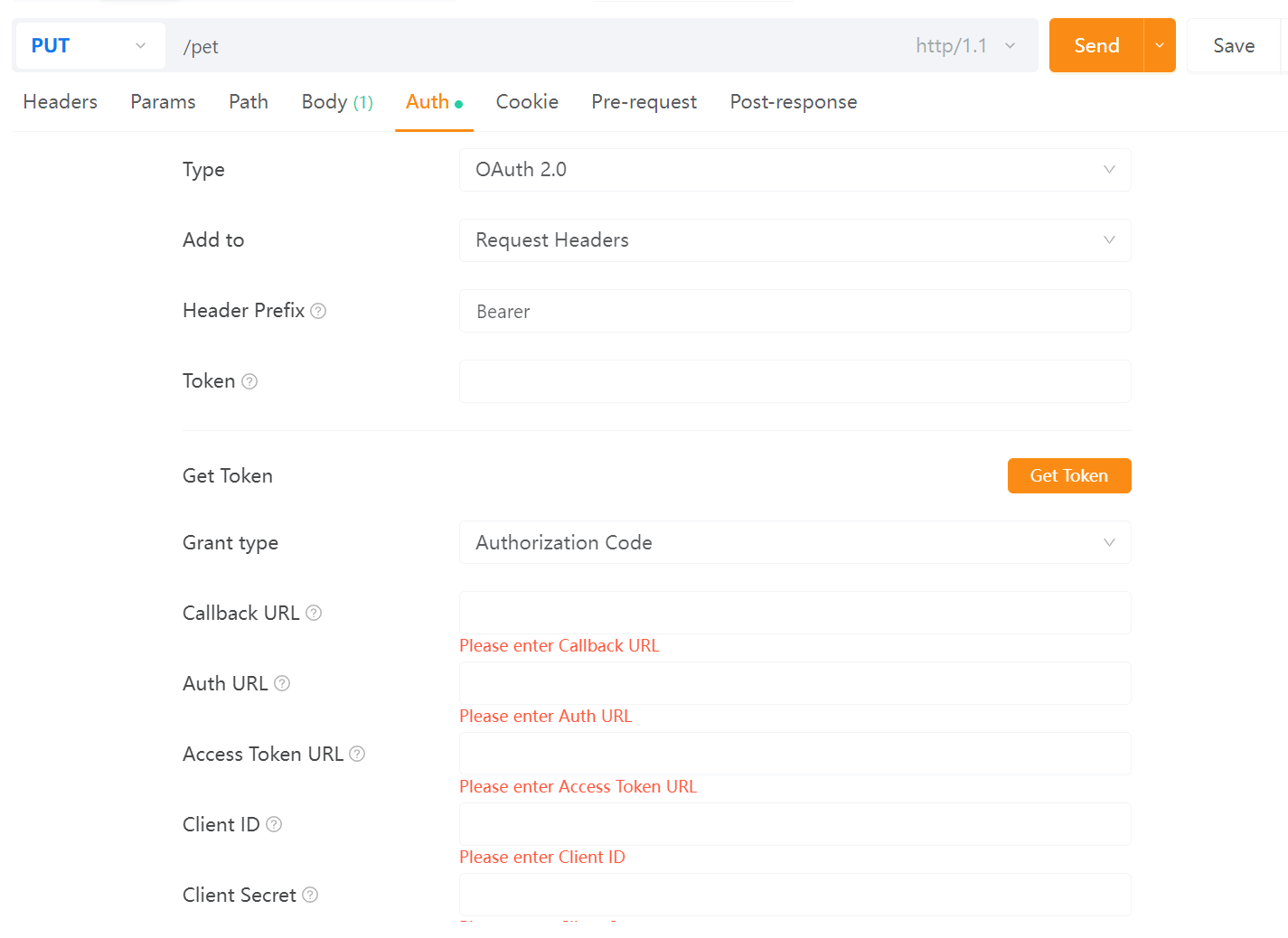
Step 3: Retrieve the Access Token
If all entered details are accurate, you will successfully generate an access token. EchoAPI automatically incorporates this token into your requests, streamlining your testing process.
In addition, you can track the token’s expiration time within the tool, and options are available to reissue or revoke tokens as necessary, enhancing convenience.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the basics of OAuth 2.0 and its authentication flow. OAuth 2.0 is widely recognized as the industry standard for API authentication and, when implemented properly, helps protect user privacy and secure resource access.
OAuth 2.0 primarily consists of four authentication types (grant types):
- Authorization Code Grant
- Implicit Grant
- Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant
- Client Credentials Grant
The choice among these grant types depends on the client type, security requirements, and user experience. Generally, the Authorization Code Grant is recommended for its balance of security and usability.
By utilizing EchoAPI for testing APIs that rely on OAuth 2.0, you can streamline your development process and enhance efficiency. Understanding the OAuth 2.0 authentication flow and selecting the appropriate grant type is crucial for developing secure and user-friendly APIs. Leveraging convenient tools like EchoAPI facilitates effective API testing and accelerates your development efforts.
