Understanding and Using HTTP Methods: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the backbone of data communication for the World Wide Web. Among its core elements are HTTP methods, which define the types of requests that can be made to a server and the operations to be performed on the specified resources. The primary HTTP methods include GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. This article will delve into these methods, exploring their significance, functions, practical usage, real-world scenarios, and how to utilize them with EchoAPI for API testing.

What Are HTTP Methods?
HTTP methods are standardized instructions used to request and interact with resources on a web server. Each method directs the server to perform a specific action, ensuring that the interaction between the client and server follows a known and consistent protocol.
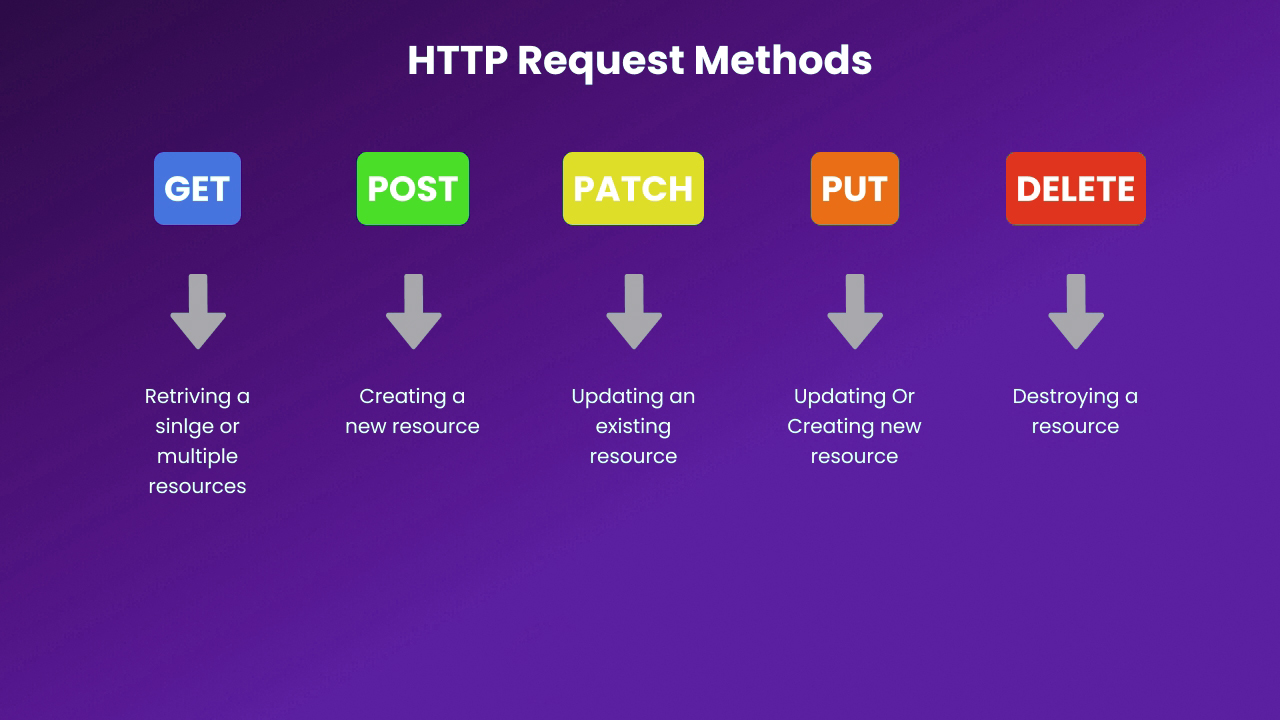
The Significance and Functions of HTTP Methods
GET Method
The GET method requests data from a specified resource. It is safe, idempotent, and cacheable, making it ideal for querying data without causing any side effects.
Significance:
- Read-Only Data Retrieval: GET is used to fetch data without modifying it.
- Cachability: Responses to GET requests can be cached, improving performance.
- Safety and Idempotency: Multiple identical requests have no additional effect, ensuring stability in repeated operations.
Usage Example:
GET /users/123 HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Scenario: Retrieving user information from an API endpoint.
POST Method
The POST method submits data to the server, often resulting in the creation of a new resource. Unlike GET, POST is neither safe nor idempotent.
Significance:
- Data Submission: Used for sending data to the server, such as submitting form data.
- Resource Creation: Creates new resources based on the submitted data.
- Non-idempotency: Each request can have different outcomes, useful for operations that need to record state.
Usage Example:
POST /users HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
Scenario: Creating a new user in the system.
PUT Method
The PUT method updates a resource or creates it if it does not exist. This method is idempotent, meaning multiple identical requests result in the same state.
Significance:
- Resource Update: Ideal for updating existing resources.
- Idempotency: Ensures consistent results with repeated requests.
- Full Replacement: Often replaces the entire resource with the provided data.
Usage Example:
PUT /users/123 HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "Jane Doe",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
Scenario: Updating existing user information.
DELETE Method
The DELETE method removes a specified resource from the server. Like GET and PUT, it is idempotent.
Significance:
- Resource Deletion: Removes resources from the server.
- Idempotency: Ensures the resource is deleted once, regardless of how many times the request is made.
- State Management: Helps in managing resource lifecycle by allowing clean deletion.
Usage Example:
DELETE /users/123 HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Scenario: Deleting a user from the system.
Practicing HTTP Methods with EchoAPI
EchoAPI is a valuable tool for testing and debugging API endpoints with various HTTP methods. Let's explore how to use EchoAPI for these methods.
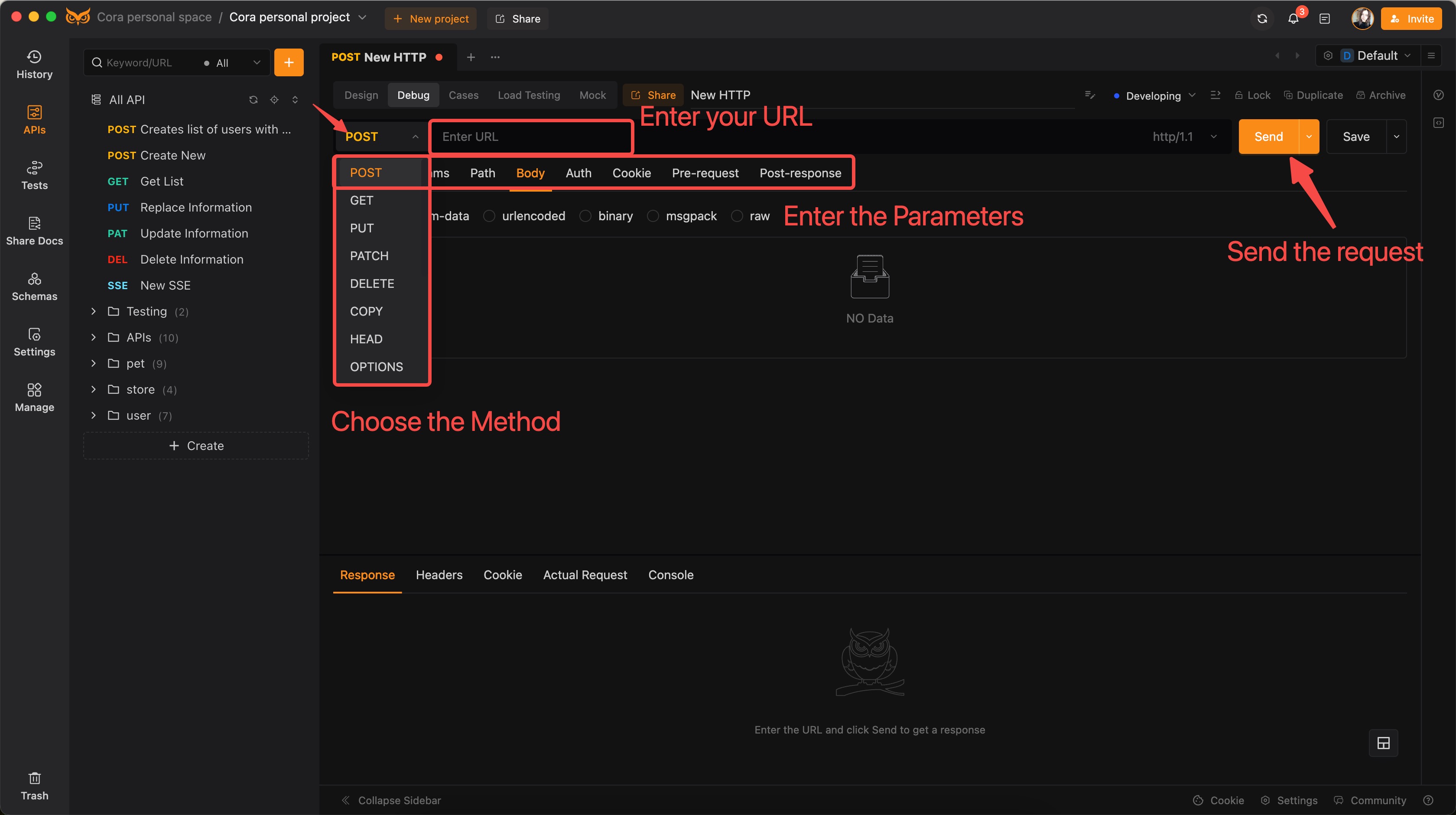
1. Testing API by Filling URL and Parameters
EchoAPI provides a user-friendly interface that allows you to manually enter the URL and parameters to test your API endpoints.
2. Testing API Using cURL Command
EchoAPI allows you to directly import and execute cURL commands for quick and efficient API testing.
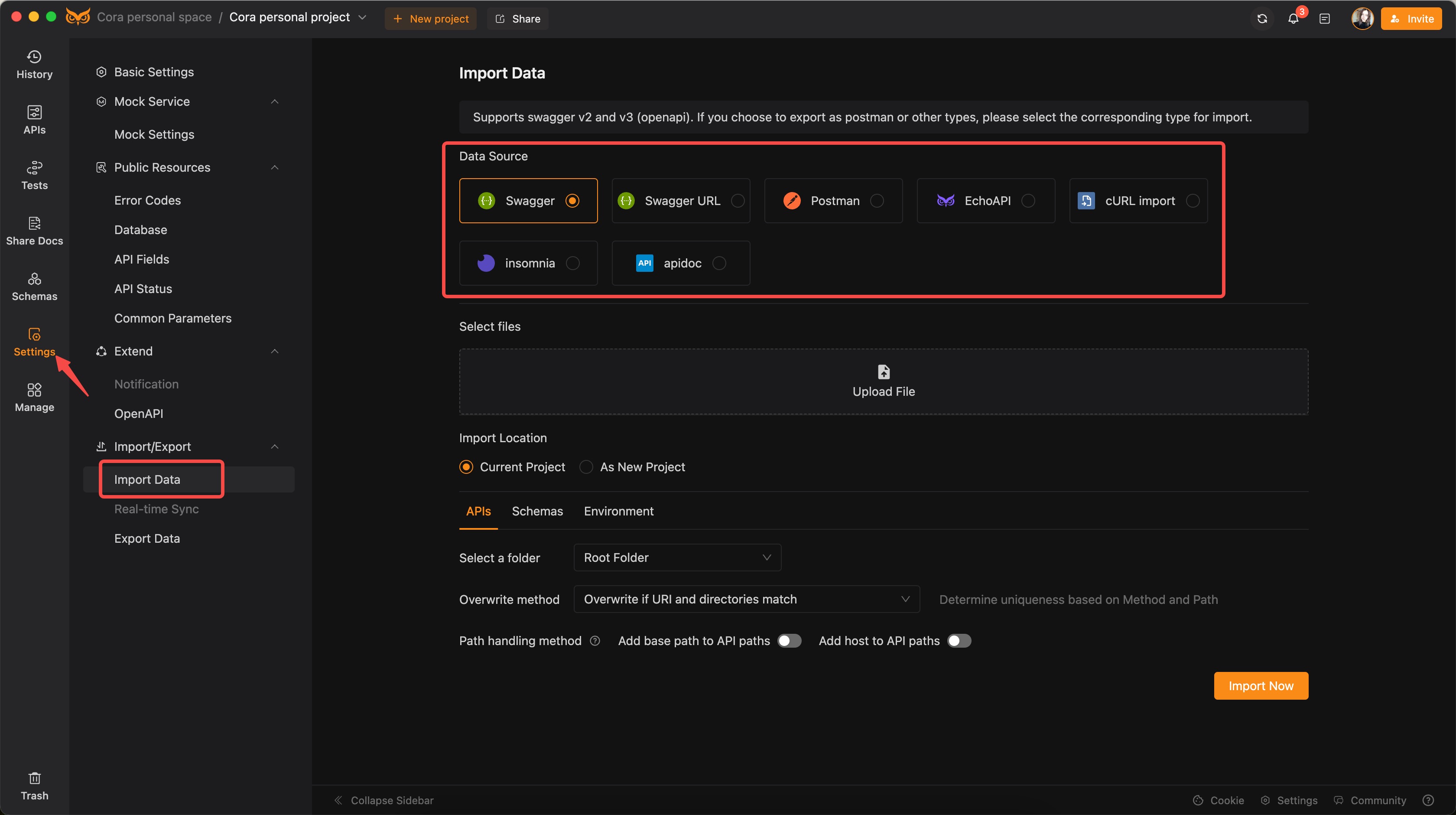
3. Importing Projects for API Testing
EchoAPI supports the import of projects from popular API documentation tools such as Postman, Swagger, Insomnia, and Apidoc. This feature is perfect for large teams and complex projects.
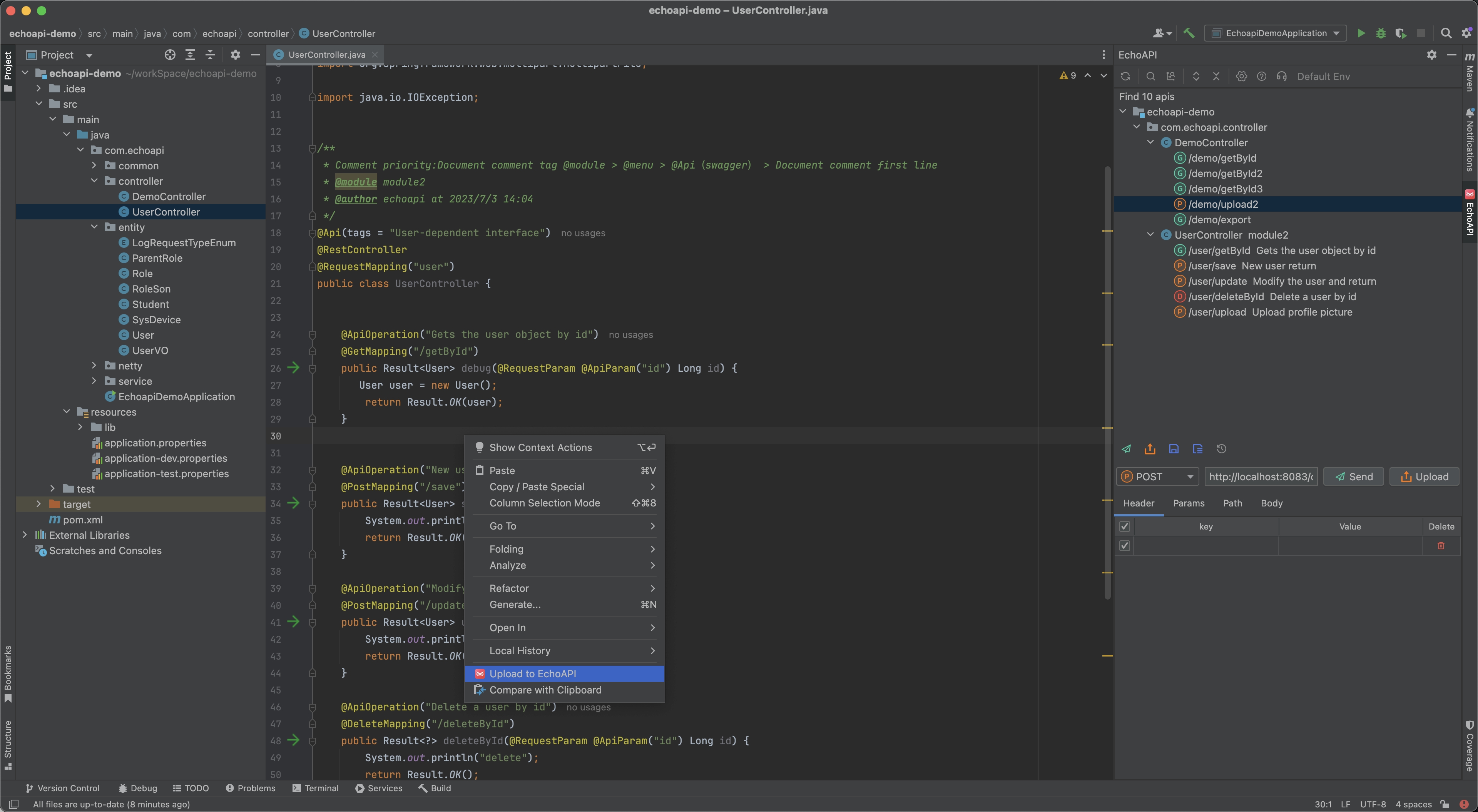
4. Syncing API via EchoAPI Helper (IDEA-Plugin)
EchoAPI offers an IntelliJ IDEA plugin that allows seamless synchronization of API definitions directly from your codebase into EchoAPI.
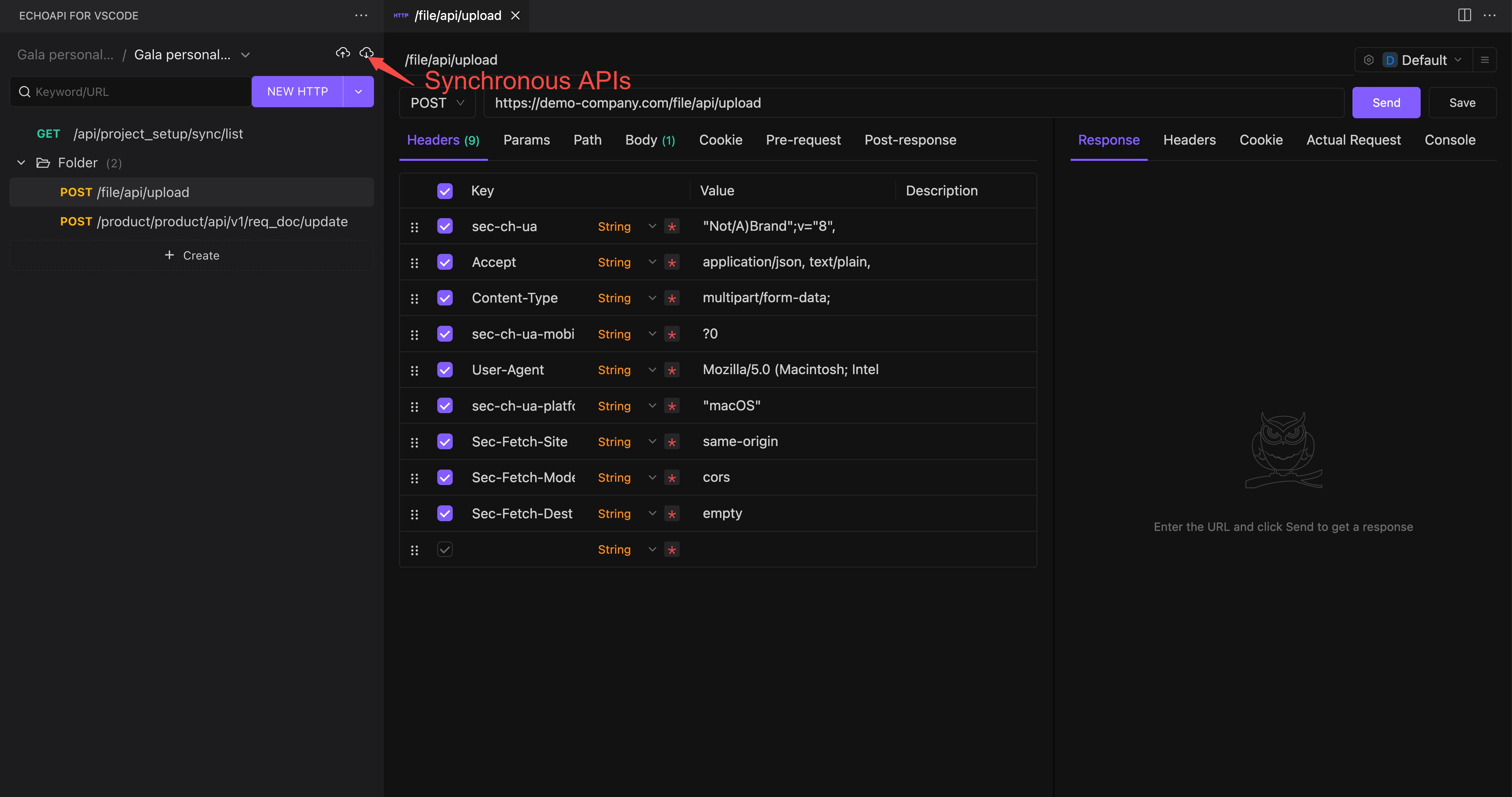
5. Syncing API via EchoAPI for Vscode (VS Code-Plugin)
For Visual Studio Code users, EchoAPI provides a plugin to sync APIs defined within the VS Code environment.
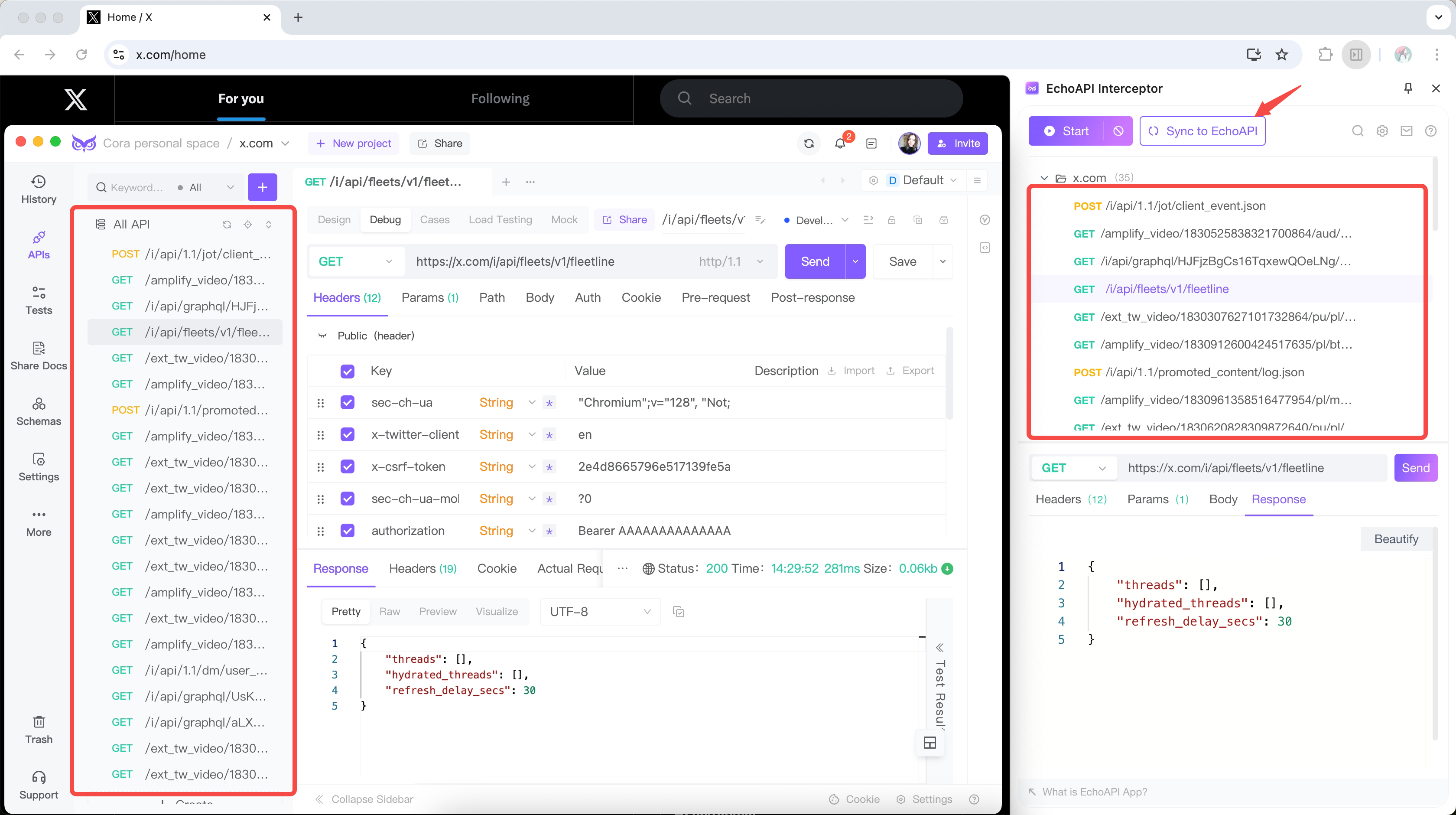
6. Syncing API via EchoAPI Interceptor(Chrome-Plugin)
EchoAPI has developed EchoAPI Interceptor that can capture API requests and sync them to EchoAPI for testing.
Conclusion
Understanding and correctly implementing HTTP methods are crucial for developing robust web applications and APIs. Each method has a unique role in resource manipulation:
- GET: Safe data retrieval,
- POST: Data submission and resource creation,
- PUT: Idempotent resource updates,
- DELETE: Resource removal.
By leveraging tools like EchoAPI, developers can test and debug their endpoints efficiently, ensuring their correctness and reliability. Mastering these methods enhances the capability to build effective and maintainable web services, ultimately benefiting the business by providing a seamless and secure user experience.
